Food Processing
Heat Exchangers
Heat exchangers play a critically important role in food processing, helping ensure safety, preserving quality, and improving the efficiency across a broad spectrum of applications. In the food industry, they are primarily used for heating or cooling products as needed during preparation and packaging. One of the most common uses is pasteurization, where heat exchangers enable the precise temperature control necessary to eliminate pathogens from beverages like milk, juice, and beer without negatively impacting taste or nutritional value.
Heat exchangers also contribute to processes like wort cooling in beer production, ultra-high temperature sterilization for longer shelf life, and the delicate task of maintaining the quality of temperature-sensitive produce like honey. Furthermore, they are integral to Clean In Place (CIP) systems, which automate cleaning and disinfecting without dismantling equipment, thereby enhancing efficiency and ensuring rigorous hygiene standards.
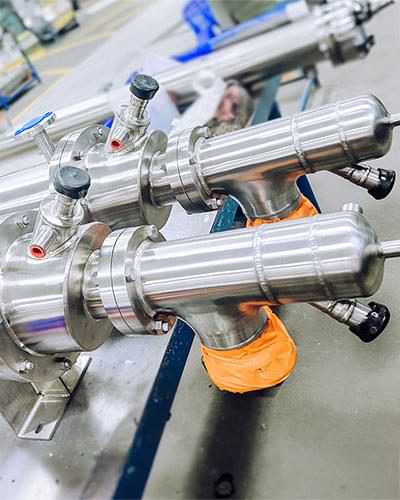

Food Processing Heat Exchangers
- Enhanced Safety: Achieve pathogen-free consumables while maintaining food standards.
- Energy Efficiency: Recycle heat in processing, reducing energy consumption significantly.
- Product Quality: Ensure gentle handling for minimal impact on flavor, nutrients, and consistency.
- Precision Control: Manage exact temperature requirements for complex processes.
MARKETS

Engine Cooling

Hydraulic Cooling

Process Cooling

Compressor Aftercoolers
Condensers

Irrigation Coolers

Injection Molding



